Aeromodelling, the hobby of designing, building, and flying model aircraft, is a blend of art and science. The choice of materials plays a crucial role in the strength, durability, and performance of the models. This guide delves into the different kinds of wood, adhesives, paint, and dope used in aeromodelling to construct and enhance the strength of aeromodels.
1. Types of Wood Used in Aeromodelling
Wood is the primary material for constructing aeromodels due to its lightweight and strong properties. Here are the common types of wood used:
Balsa Wood

Properties:
- Lightweight: Balsa is one of the lightest woods available, making it ideal for flight.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: It has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, providing good structural support without adding excessive weight.
Uses:
- Airframe Construction: The main structure of the aircraft, including fuselage, wings, and tail sections.
- Skinning: Covering larger surfaces to create a smooth, aerodynamic finish.
Basswood

Properties:
- Moderate Weight: Heavier than balsa but stronger, providing a good balance of strength and weight.
- Ease of Work: Basswood is easy to cut, sand, and glue.
Uses:
- Reinforcements: Strengthening critical areas like wing spars and fuselage longerons.
- Detail Work: Creating small, detailed components that require precision.
Plywood

Properties:
- High Strength: Plywood is strong and resistant to warping.
- Multiple Layers: Made by gluing together thin layers of wood, which increases its durability and strength.
Uses:
- Structural Components: Bulkheads, formers, and other high-stress areas.
- Mounting Points: Motor mounts and landing gear attachment points.
2. Adhesives Used in Aeromodelling
Choosing the right adhesive is critical for ensuring the integrity and strength of the model. Here are the common adhesives used:
Cyanoacrylate (CA) Glue

Properties:
- Quick Setting: Bonds almost instantly, allowing for rapid construction.
- Strong Bond: Provides a very strong joint for most types of wood.
Uses:
- General Assembly: Quick bonding of parts where immediate strength is needed.
- Field Repairs: Quick fixes during flying sessions.
Epoxy Resin

Properties:
- High Strength: Creates extremely strong bonds, suitable for high-stress areas.
- Gap-Filling: Can fill gaps and provide structural support.
Uses:
- Critical Joints: Areas that endure high loads, such as wing joints and motor mounts.
- Reinforcements: Bonding materials like fiberglass or carbon fiber to wooden structures.
Aliphatic Resin (Wood Glue)

Properties:
- Strong Bond: Provides a durable bond that is slightly flexible.
- Sandable: Dries clear and can be sanded smooth.
Uses:
- General Construction: Ideal for wood-to-wood joints in the main structure.
- Laminating: Gluing layers of wood together, such as in plywood construction.
Polyurethane Glue

Properties:
- Expanding Bond: Expands as it cures, filling gaps and creating a strong joint.
- Waterproof: Resistant to moisture, making it suitable for outdoor models.
Uses:
- High-Stress Areas: Joints that require maximum strength and durability.
- Water-Resistant Joints: Components exposed to moisture or humidity.
3. Paints Used in Aeromodelling
Paint not only enhances the appearance of the model but also protects the wood from moisture and environmental damage.
Acrylic Paint

Properties:
- Water-Based: Easy to clean up and environmentally friendly.
- Quick Drying: Dries quickly, allowing for fast progress.
Uses:
- Detailing: Adding intricate details and designs.
- Base Coats: Providing a smooth, even base layer before applying other finishes.
Enamel Paint

Properties:
- Durable Finish: Provides a hard, glossy finish that is resistant to wear.
- Oil-Based: Takes longer to dry but offers a tougher surface.
Uses:
- Final Coats: Applying a durable topcoat that protects the model.
- Detailing: Creating smooth, glossy finishes for specific parts.
Spray Paint

Properties:
- Even Coverage: Provides a smooth, even coat over large areas.
- Quick Application: Allows for fast application, especially on large surfaces.
Uses:
- Large Surfaces: Covering wings and fuselage with a uniform finish.
- Base Coats: Laying down an even base before detailed painting.
4. Dope Used in Aeromodelling
Dope is a special lacquer that strengthens and tightens the covering material on aeromodels. It is essential for finishing and protecting the model.
Nitrate Dope

Properties:
- Strong and Durable: Provides a hard, durable finish that strengthens the covering material.
- Quick Drying: Dries quickly, allowing for multiple coats in a short time.
Uses:
- Base Coats: Applying to bare wood and fabric to create a strong base.
- Strengthening: Adding rigidity and strength to the covering material.
Butyrate Dope

Properties:
- Flexible and Resistant: Offers more flexibility and better resistance to cracking than nitrate dope.
- UV Protection: Protects the model from ultraviolet light, preventing damage from the sun.
Uses:
- Final Coats: Applying over nitrate dope for a durable, flexible finish.
- Protective Coating: Providing UV protection for outdoor models.
Enhancing Strength and Durability
In addition to selecting the right materials, there are several techniques and additional materials that can enhance the strength and durability of your aeromodels:
Fiberglass Reinforcement
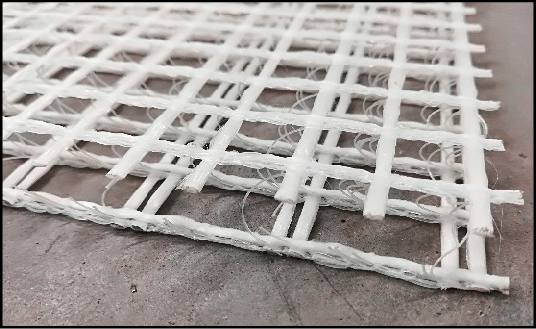
Uses:
- Wing Spars and Fuselage: Applying fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin to high-stress areas for added strength.
- Surface Reinforcement: Strengthening areas prone to wear and tear.
Carbon Fiber

Uses:
- Structural Reinforcement: Using carbon fiber rods and sheets in critical areas to add strength without significant weight increase.
- Control Rods: Creating lightweight, strong control linkages.
Kevlar

Uses:
- Impact Protection: Adding Kevlar to areas prone to impacts, such as leading edges of wings.
- Reinforcement: Strengthening high-stress joints and connections.
Conclusion
Aeromodelling is a rewarding hobby that combines craftsmanship, creativity, and a love for aviation. By choosing the right materials—wood, adhesives, paint, and dope—you can build models that are not only beautiful but also strong and durable. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced modeller, understanding the properties and uses of these materials will help you create aeromodels that fly well and stand the test of time. So, gather your materials, and let your imagination take flight!



Leave a Reply